이 포스팅은 Kaggle::Titanic 시리즈 10 편 중 10 번째 글 입니다.
목차
Kaggle에 있는 Titanic Prediction 문제의 모델들을 앙상블하는 방법을 알아본다.
앙상블
여러개의 모델을 만들고, 이것들의 결과들을 투표하는 방식으로 합치자.
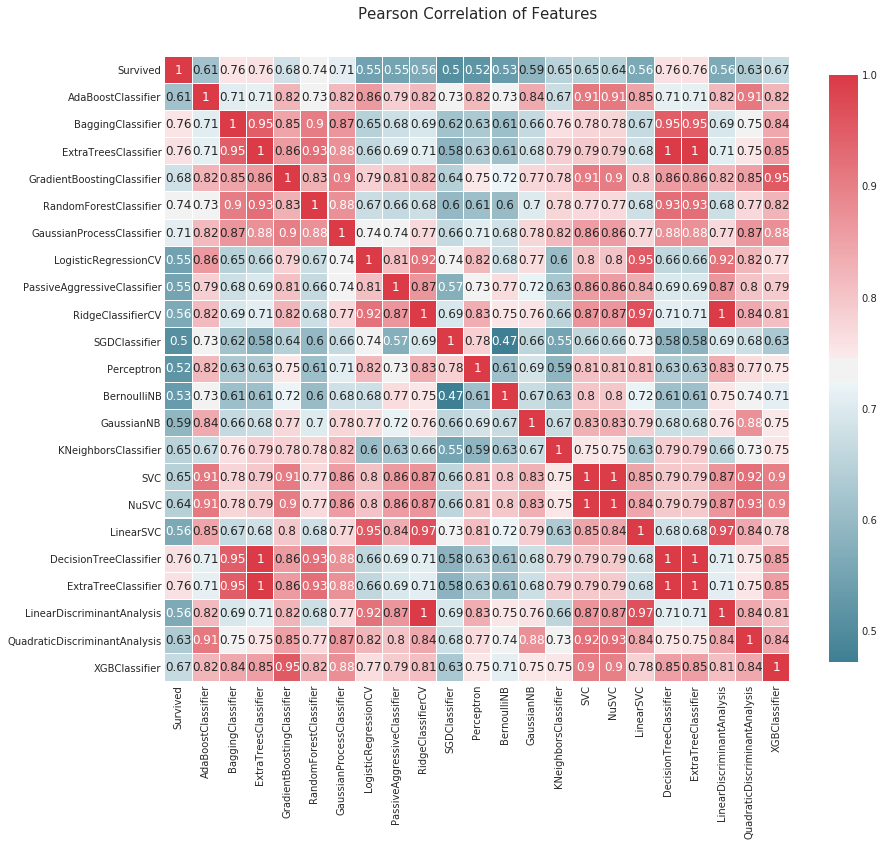
모델의 정확도간의 상관계수
#compare algorithm predictions with each other, where 1 = exactly similar and 0 = exactly opposite
#there are some 1's, but enough blues and light reds to create a "super algorithm" by combining them
correlation_heatmap(MLA_predict)
Hard Vote (다수결) & Soft Vote (가중치)
#why choose one model, when you can pick them all with voting classifier
#http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.VotingClassifier.html
#removed models w/o attribute 'predict_proba' required for vote classifier and models with a 1.0 correlation to another model
vote_est = [
#Ensemble Methods: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/ensemble.html
('ada', ensemble.AdaBoostClassifier()),
('bc', ensemble.BaggingClassifier()),
('etc',ensemble.ExtraTreesClassifier()),
('gbc', ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier()),
('rfc', ensemble.RandomForestClassifier()),
#Gaussian Processes: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/gaussian_process.html#gaussian-process-classification-gpc
('gpc', gaussian_process.GaussianProcessClassifier()),
#GLM: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/linear_model.html#logistic-regression
('lr', linear_model.LogisticRegressionCV()),
#Navies Bayes: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/naive_bayes.html
('bnb', naive_bayes.BernoulliNB()),
('gnb', naive_bayes.GaussianNB()),
#Nearest Neighbor: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/neighbors.html
('knn', neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier()),
#SVM: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/svm.html
('svc', svm.SVC(probability=True)),
#xgboost: http://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest/model.html
('xgb', XGBClassifier())
]
#Hard Vote or majority rules, 이 부분 코드가 약간 이해가 안되지만 일단 넘어간다.
vote_hard = ensemble.VotingClassifier(estimators = vote_est , voting = 'hard')
vote_hard_cv = model_selection.cross_validate(vote_hard, data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target], cv = cv_split)
vote_hard.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
print("Hard Voting Training w/bin score mean: {:.2f}". format(vote_hard_cv['train_score'].mean()*100))
print("Hard Voting Test w/bin score mean: {:.2f}". format(vote_hard_cv['test_score'].mean()*100))
print("Hard Voting Test w/bin score 3*std: +/- {:.2f}". format(vote_hard_cv['test_score'].std()*100*3))
print('-'*10)
#Soft Vote or weighted probabilities
vote_soft = ensemble.VotingClassifier(estimators = vote_est , voting = 'soft')
vote_soft_cv = model_selection.cross_validate(vote_soft, data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target], cv = cv_split)
vote_soft.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
print("Soft Voting Training w/bin score mean: {:.2f}". format(vote_soft_cv['train_score'].mean()*100))
print("Soft Voting Test w/bin score mean: {:.2f}". format(vote_soft_cv['test_score'].mean()*100))
print("Soft Voting Test w/bin score 3*std: +/- {:.2f}". format(vote_soft_cv['test_score'].std()*100*3))
print('-'*10)
Hard Voting Training w/bin score mean: 86.61
Hard Voting Test w/bin score mean: 82.35
Hard Voting Test w/bin score 3*std: +/- 4.91
----------
Soft Voting Training w/bin score mean: 87.21
Soft Voting Test w/bin score mean: 82.43
Soft Voting Test w/bin score 3*std: +/- 5.14
----------
Grid Search
#WARNING: Running is very computational intensive and time expensive.
#Code is written for experimental/developmental purposes and not production ready!
#Hyperparameter Tune with GridSearchCV: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.model_selection.GridSearchCV.html
grid_n_estimator = [10, 50, 100, 300]
grid_ratio = [.1, .25, .5, .75, 1.0]
grid_learn = [.01, .03, .05, .1, .25]
grid_max_depth = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, None]
grid_min_samples = [5, 10, .03, .05, .10]
grid_criterion = ['gini', 'entropy']ㅁ
grid_bool = [True, False]
grid_seed = [0]
grid_param = [
[{
#AdaBoostClassifier - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.AdaBoostClassifier.html
'n_estimators': grid_n_estimator, #default=50
'learning_rate': grid_learn, #default=1
#'algorithm': ['SAMME', 'SAMME.R'], #default=’SAMME.R
'random_state': grid_seed
}],
[{
#BaggingClassifier - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.BaggingClassifier.html#sklearn.ensemble.BaggingClassifier
'n_estimators': grid_n_estimator, #default=10
'max_samples': grid_ratio, #default=1.0
'random_state': grid_seed
}],
[{
#ExtraTreesClassifier - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.ExtraTreesClassifier.html#sklearn.ensemble.ExtraTreesClassifier
'n_estimators': grid_n_estimator, #default=10
'criterion': grid_criterion, #default=”gini”
'max_depth': grid_max_depth, #default=None
'random_state': grid_seed
}],
[{
#GradientBoostingClassifier - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier.html#sklearn.ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier
#'loss': ['deviance', 'exponential'], #default=’deviance’
'learning_rate': [.05], #default=0.1 -- 12/31/17 set to reduce runtime -- The best parameter for GradientBoostingClassifier is {'learning_rate': 0.05, 'max_depth': 2, 'n_estimators': 300, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 264.45 seconds.
'n_estimators': [300], #default=100 -- 12/31/17 set to reduce runtime -- The best parameter for GradientBoostingClassifier is {'learning_rate': 0.05, 'max_depth': 2, 'n_estimators': 300, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 264.45 seconds.
#'criterion': ['friedman_mse', 'mse', 'mae'], #default=”friedman_mse”
'max_depth': grid_max_depth, #default=3
'random_state': grid_seed
}],
[{
#RandomForestClassifier - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier.html#sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier
'n_estimators': grid_n_estimator, #default=10
'criterion': grid_criterion, #default=”gini”
'max_depth': grid_max_depth, #default=None
'oob_score': [True], #default=False -- 12/31/17 set to reduce runtime -- The best parameter for RandomForestClassifier is {'criterion': 'entropy', 'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 100, 'oob_score': True, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 146.35 seconds.
'random_state': grid_seed
}],
[{
#GaussianProcessClassifier
'max_iter_predict': grid_n_estimator, #default: 100
'random_state': grid_seed
}],
[{
#LogisticRegressionCV - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegressionCV.html#sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegressionCV
'fit_intercept': grid_bool, #default: True
#'penalty': ['l1','l2'],
'solver': ['newton-cg', 'lbfgs', 'liblinear', 'sag', 'saga'], #default: lbfgs
'random_state': grid_seed
}],
[{
#BernoulliNB - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.naive_bayes.BernoulliNB.html#sklearn.naive_bayes.BernoulliNB
'alpha': grid_ratio, #default: 1.0
}],
#GaussianNB -
[{}],
[{
#KNeighborsClassifier - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier.html#sklearn.neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier
'n_neighbors': [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], #default: 5
'weights': ['uniform', 'distance'], #default = ‘uniform’
'algorithm': ['auto', 'ball_tree', 'kd_tree', 'brute']
}],
[{
#SVC - http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.svm.SVC.html#sklearn.svm.SVC
#http://blog.hackerearth.com/simple-tutorial-svm-parameter-tuning-python-r
#'kernel': ['linear', 'poly', 'rbf', 'sigmoid'],
'C': [1,2,3,4,5], #default=1.0
'gamma': grid_ratio, #edfault: auto
'decision_function_shape': ['ovo', 'ovr'], #default:ovr
'probability': [True],
'random_state': grid_seed
}],
[{
#XGBClassifier - http://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest/parameter.html
'learning_rate': grid_learn, #default: .3
'max_depth': [1,2,4,6,8,10], #default 2
'n_estimators': grid_n_estimator,
'seed': grid_seed
}]
]
start_total = time.perf_counter() #https://docs.python.org/3/library/time.html#time.perf_counter
for clf, param in zip (vote_est, grid_param): #https://docs.python.org/3/library/functions.html#zip
#print(clf[1]) #vote_est is a list of tuples, index 0 is the name and index 1 is the algorithm
#print(param)
start = time.perf_counter()
best_search = model_selection.GridSearchCV(estimator = clf[1], param_grid = param, cv = cv_split, scoring = 'roc_auc')
best_search.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
run = time.perf_counter() - start
best_param = best_search.best_params_
print('The best parameter for {} is {} with a runtime of {:.2f} seconds.'.format(clf[1].__class__.__name__, best_param, run))
clf[1].set_params(**best_param)
run_total = time.perf_counter() - start_total
print('Total optimization time was {:.2f} minutes.'.format(run_total/60))
print('-'*10)
The best parameter for AdaBoostClassifier is {'learning_rate': 0.1, 'n_estimators': 300, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 37.28 seconds.
The best parameter for BaggingClassifier is {'max_samples': 0.25, 'n_estimators': 300, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 33.04 seconds.
The best parameter for ExtraTreesClassifier is {'criterion': 'entropy', 'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 100, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 68.93 seconds.
The best parameter for GradientBoostingClassifier is {'learning_rate': 0.05, 'max_depth': 2, 'n_estimators': 300, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 38.77 seconds.
The best parameter for RandomForestClassifier is {'criterion': 'entropy', 'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 100, 'oob_score': True, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 84.14 seconds.
The best parameter for GaussianProcessClassifier is {'max_iter_predict': 10, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 6.19 seconds.
The best parameter for LogisticRegressionCV is {'fit_intercept': True, 'random_state': 0, 'solver': 'liblinear'} with a runtime of 9.40 seconds.
The best parameter for BernoulliNB is {'alpha': 0.1} with a runtime of 0.24 seconds.
The best parameter for GaussianNB is {} with a runtime of 0.05 seconds.
The best parameter for KNeighborsClassifier is {'algorithm': 'brute', 'n_neighbors': 7, 'weights': 'uniform'} with a runtime of 5.56 seconds.
The best parameter for SVC is {'C': 2, 'decision_function_shape': 'ovo', 'gamma': 0.1, 'probability': True, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 30.49 seconds.
The best parameter for XGBClassifier is {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'max_depth': 4, 'n_estimators': 300, 'seed': 0} with a runtime of 43.57 seconds.
Total optimization time was 5.96 minutes.
----------
vote로 들어간 추정기 각각에 대해 최적 param을 찾는다.
앙상블
최적의 추정기들에 대해 마지막으로 Voting을 수행한다.
#Hard Vote or majority rules w/Tuned Hyperparameters
grid_hard = ensemble.VotingClassifier(estimators = vote_est , voting = 'hard')
grid_hard_cv = model_selection.cross_validate(grid_hard, data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target], cv = cv_split)
grid_hard.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
print("Hard Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Training w/bin score mean: {:.2f}". format(grid_hard_cv['train_score'].mean()*100))
print("Hard Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Test w/bin score mean: {:.2f}". format(grid_hard_cv['test_score'].mean()*100))
print("Hard Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Test w/bin score 3*std: +/- {:.2f}". format(grid_hard_cv['test_score'].std()*100*3))
print('-'*10)
#Soft Vote or weighted probabilities w/Tuned Hyperparameters
grid_soft = ensemble.VotingClassifier(estimators = vote_est , voting = 'soft')
grid_soft_cv = model_selection.cross_validate(grid_soft, data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target], cv = cv_split)
grid_soft.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
print("Soft Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Training w/bin score mean: {:.2f}". format(grid_soft_cv['train_score'].mean()*100))
print("Soft Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Test w/bin score mean: {:.2f}". format(grid_soft_cv['test_score'].mean()*100))
print("Soft Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Test w/bin score 3*std: +/- {:.2f}". format(grid_soft_cv['test_score'].std()*100*3))
print('-'*10)
#12/31/17 tuned with data1_x_bin
#The best parameter for AdaBoostClassifier is {'learning_rate': 0.1, 'n_estimators': 300, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 33.39 seconds.
#The best parameter for BaggingClassifier is {'max_samples': 0.25, 'n_estimators': 300, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 30.28 seconds.
#The best parameter for ExtraTreesClassifier is {'criterion': 'entropy', 'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 100, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 64.76 seconds.
#The best parameter for GradientBoostingClassifier is {'learning_rate': 0.05, 'max_depth': 2, 'n_estimators': 300, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 34.35 seconds.
#The best parameter for RandomForestClassifier is {'criterion': 'entropy', 'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 100, 'oob_score': True, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 76.32 seconds.
#The best parameter for GaussianProcessClassifier is {'max_iter_predict': 10, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 6.01 seconds.
#The best parameter for LogisticRegressionCV is {'fit_intercept': True, 'random_state': 0, 'solver': 'liblinear'} with a runtime of 8.04 seconds.
#The best parameter for BernoulliNB is {'alpha': 0.1} with a runtime of 0.19 seconds.
#The best parameter for GaussianNB is {} with a runtime of 0.04 seconds.
#The best parameter for KNeighborsClassifier is {'algorithm': 'brute', 'n_neighbors': 7, 'weights': 'uniform'} with a runtime of 4.84 seconds.
#The best parameter for SVC is {'C': 2, 'decision_function_shape': 'ovo', 'gamma': 0.1, 'probability': True, 'random_state': 0} with a runtime of 29.39 seconds.
#The best parameter for XGBClassifier is {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'max_depth': 4, 'n_estimators': 300, 'seed': 0} with a runtime of 46.23 seconds.
#Total optimization time was 5.56 minutes.
Hard Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Training w/bin score mean: 85.22
Hard Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Test w/bin score mean: 82.31
Hard Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Test w/bin score 3*std: +/- 5.26
----------
Soft Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Training w/bin score mean: 84.76
Soft Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Test w/bin score mean: 82.28
Soft Voting w/Tuned Hyperparameters Test w/bin score 3*std: +/- 5.42
----------
실제 validation에 적용 (for submit)
#prepare data for modeling
print(data_val.info())
print("-"*10)
#data_val.sample(10)
#handmade decision tree - submission score = 0.77990
data_val['Survived'] = mytree(data_val).astype(int)
#decision tree w/full dataset modeling submission score: defaults= 0.76555, tuned= 0.77990
#submit_dt = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
#submit_dt = model_selection.GridSearchCV(tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(), param_grid=param_grid, scoring = 'roc_auc', cv = cv_split)
#submit_dt.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
#print('Best Parameters: ', submit_dt.best_params_) #Best Parameters: {'criterion': 'gini', 'max_depth': 4, 'random_state': 0}
#data_val['Survived'] = submit_dt.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
#bagging w/full dataset modeling submission score: defaults= 0.75119, tuned= 0.77990
#submit_bc = ensemble.BaggingClassifier()
#submit_bc = model_selection.GridSearchCV(ensemble.BaggingClassifier(), param_grid= {'n_estimators':grid_n_estimator, 'max_samples': grid_ratio, 'oob_score': grid_bool, 'random_state': grid_seed}, scoring = 'roc_auc', cv = cv_split)
#submit_bc.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
#print('Best Parameters: ', submit_bc.best_params_) #Best Parameters: {'max_samples': 0.25, 'n_estimators': 500, 'oob_score': True, 'random_state': 0}
#data_val['Survived'] = submit_bc.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
#extra tree w/full dataset modeling submission score: defaults= 0.76555, tuned= 0.77990
#submit_etc = ensemble.ExtraTreesClassifier()
#submit_etc = model_selection.GridSearchCV(ensemble.ExtraTreesClassifier(), param_grid={'n_estimators': grid_n_estimator, 'criterion': grid_criterion, 'max_depth': grid_max_depth, 'random_state': grid_seed}, scoring = 'roc_auc', cv = cv_split)
#submit_etc.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
#print('Best Parameters: ', submit_etc.best_params_) #Best Parameters: {'criterion': 'entropy', 'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 100, 'random_state': 0}
#data_val['Survived'] = submit_etc.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
#random foreset w/full dataset modeling submission score: defaults= 0.71291, tuned= 0.73205
#submit_rfc = ensemble.RandomForestClassifier()
#submit_rfc = model_selection.GridSearchCV(ensemble.RandomForestClassifier(), param_grid={'n_estimators': grid_n_estimator, 'criterion': grid_criterion, 'max_depth': grid_max_depth, 'random_state': grid_seed}, scoring = 'roc_auc', cv = cv_split)
#submit_rfc.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
#print('Best Parameters: ', submit_rfc.best_params_) #Best Parameters: {'criterion': 'entropy', 'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 100, 'random_state': 0}
#data_val['Survived'] = submit_rfc.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
#ada boosting w/full dataset modeling submission score: defaults= 0.74162, tuned= 0.75119
#submit_abc = ensemble.AdaBoostClassifier()
#submit_abc = model_selection.GridSearchCV(ensemble.AdaBoostClassifier(), param_grid={'n_estimators': grid_n_estimator, 'learning_rate': grid_ratio, 'algorithm': ['SAMME', 'SAMME.R'], 'random_state': grid_seed}, scoring = 'roc_auc', cv = cv_split)
#submit_abc.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
#print('Best Parameters: ', submit_abc.best_params_) #Best Parameters: {'algorithm': 'SAMME.R', 'learning_rate': 0.1, 'n_estimators': 300, 'random_state': 0}
#data_val['Survived'] = submit_abc.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
#gradient boosting w/full dataset modeling submission score: defaults= 0.75119, tuned= 0.77033
#submit_gbc = ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier()
#submit_gbc = model_selection.GridSearchCV(ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(), param_grid={'learning_rate': grid_ratio, 'n_estimators': grid_n_estimator, 'max_depth': grid_max_depth, 'random_state':grid_seed}, scoring = 'roc_auc', cv = cv_split)
#submit_gbc.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
#print('Best Parameters: ', submit_gbc.best_params_) #Best Parameters: {'learning_rate': 0.25, 'max_depth': 2, 'n_estimators': 50, 'random_state': 0}
#data_val['Survived'] = submit_gbc.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
#extreme boosting w/full dataset modeling submission score: defaults= 0.73684, tuned= 0.77990
#submit_xgb = XGBClassifier()
#submit_xgb = model_selection.GridSearchCV(XGBClassifier(), param_grid= {'learning_rate': grid_learn, 'max_depth': [0,2,4,6,8,10], 'n_estimators': grid_n_estimator, 'seed': grid_seed}, scoring = 'roc_auc', cv = cv_split)
#submit_xgb.fit(data1[data1_x_bin], data1[Target])
#print('Best Parameters: ', submit_xgb.best_params_) #Best Parameters: {'learning_rate': 0.01, 'max_depth': 4, 'n_estimators': 300, 'seed': 0}
#data_val['Survived'] = submit_xgb.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
#hard voting classifier w/full dataset modeling submission score: defaults= 0.75598, tuned = 0.77990
#data_val['Survived'] = vote_hard.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
data_val['Survived'] = grid_hard.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
#soft voting classifier w/full dataset modeling submission score: defaults= 0.73684, tuned = 0.74162
#data_val['Survived'] = vote_soft.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
#data_val['Survived'] = grid_soft.predict(data_val[data1_x_bin])
#submit file
submit = data_val[['PassengerId','Survived']]
submit.to_csv("../working/submit.csv", index=False)
print('Validation Data Distribution: \n', data_val['Survived'].value_counts(normalize = True))
submit.sample(10)
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 418 entries, 0 to 417
Data columns (total 21 columns):
PassengerId 418 non-null int64
Pclass 418 non-null int64
Name 418 non-null object
Sex 418 non-null object
Age 418 non-null float64
SibSp 418 non-null int64
Parch 418 non-null int64
Ticket 418 non-null object
Fare 418 non-null float64
Cabin 91 non-null object
Embarked 418 non-null object
FamilySize 418 non-null int64
IsAlone 418 non-null int64
Title 418 non-null object
FareBin 418 non-null category
AgeBin 418 non-null category
Sex_Code 418 non-null int64
Embarked_Code 418 non-null int64
Title_Code 418 non-null int64
AgeBin_Code 418 non-null int64
FareBin_Code 418 non-null int64
dtypes: category(2), float64(2), int64(11), object(6)
memory usage: 63.1+ KB
None
----------
Validation Data Distribution:
0 0.633971
1 0.366029
Name: Survived, dtype: float64
결론
신기하게도 다른 알고리즘 보다, 내가 만든 트리의 정확도가 실제 제출시에 더 높았다. 이것은, 훈련 데이터 셋의 분포와 제출 데이터 셋의 분포가 다름을 나타낸다. 즉, CV를 통해 모델을 학습한다 할지라도 제출용 데이터의 분포가 성능에 지대한 역할을 미친다는 것이다. 알고리즘에 의존하는 것이 아닌, 전처리와 feature engineering이 더 중요한 경우도 많다.